Revolutionizing Type 2 Diabetes Treatment: Stem Cell Therapy in India
Type 2 Diabetes Stem Cell Therapy in India is emerging as a groundbreaking approach to managing and potentially reversing the effects of this chronic metabolic disorder. As the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes continues to rise globally, traditional treatment methods often focus on symptom management rather than addressing the root cause. Stem cell therapy offers a promising alternative by targeting the underlying mechanisms of the disease, aiming to restore pancreatic function and insulin production.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
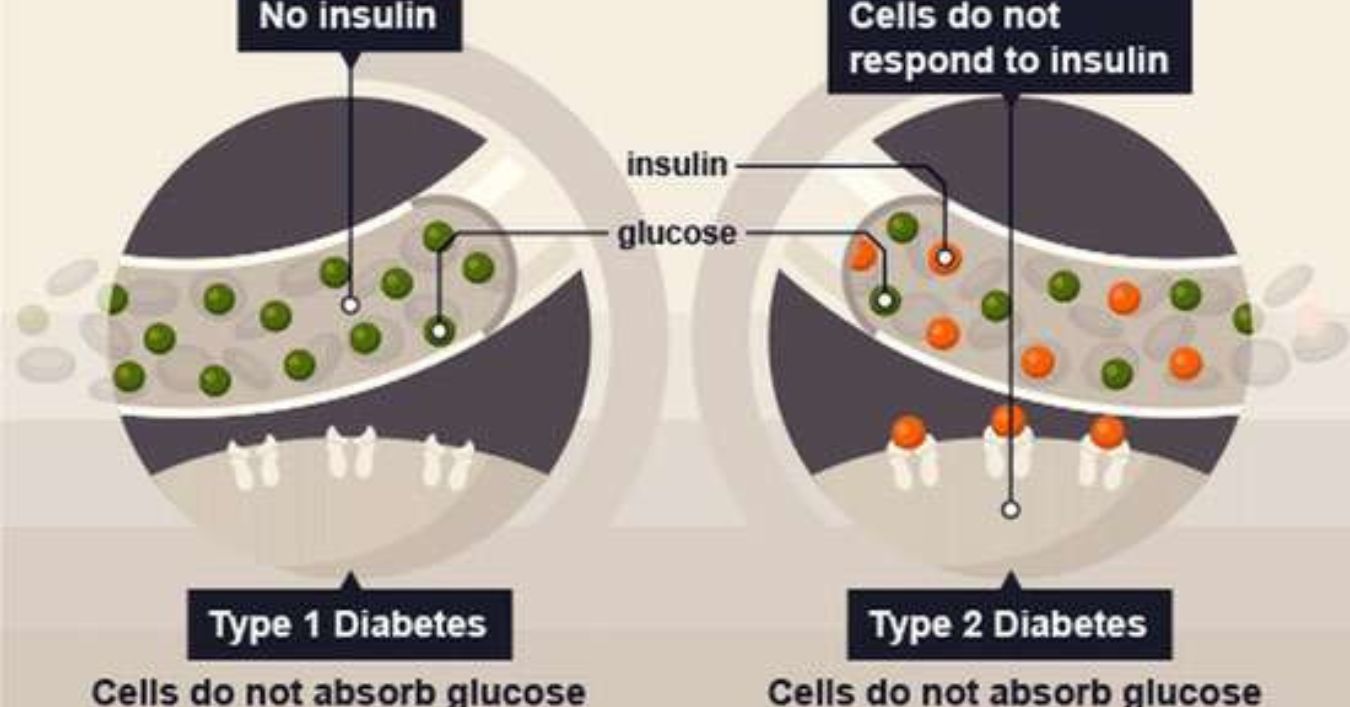
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, where the immune system attacks insulin producing cells, Type 2 diabetes involves a gradual decline in insulin sensitivity and secretion. This condition is often associated with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity.
The Role of Stem Cells in Diabetes Treatment
Stem cells possess the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, including insulin-producing beta cells. This regenerative potential makes them a focal point in diabetes research. In Type 2 diabetes, stem cell therapy aims to replenish damaged or dysfunctional beta cells, thereby improving insulin production and glucose regulation.
Types of Stem Cells Used
-
Autologous Stem Cells: These are stem cells harvested from the patient’s own body, typically from bone marrow or adipose tissue. Using autologous cells reduces the risk of immune rejection and ethical concerns associated with donor cells.
-
Allogeneic Stem Cells: Derived from a donor, these cells are used when autologous cells are not viable. However, they require careful matching to minimize the risk of immune rejection.
Stem Cell Therapy Procedure in India
In India, several medical centers have pioneered stem cell therapies for Type 2 diabetes. The procedure generally involves the following steps:
-
Stem Cell Harvesting: Stem cells are collected from the patient’s bone marrow or adipose tissue.
-
Processing and Culturing: The harvested cells are processed and cultured to increase their number and potency.
-
Cell Infusion: The prepared stem cells are then infused into the patient’s body, often through intravenous injection or direct pancreatic infusion.
-
Post-Treatment Monitoring: Patients are monitored for any adverse reactions, and regular follow up assessments are conducted to evaluate the therapy’s effectiveness.
Clinical Outcomes and Research
Clinical studies and trials have shown promising results for stem cell therapy in Type 2 diabetes patients. Many patients experience improved blood glucose control, reduced insulin dependence, and enhanced overall metabolic function. For instance, a study involving autologous bone marrow-derived stem cells demonstrated significant improvements in glycemic control and insulin sensitivity among participants.
Furthermore, research indicates that stem cell therapy can address complications associated with diabetes, such as diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy. By promoting tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation, stem cells may help mitigate these debilitating conditions.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
-
Restoration of Beta-Cell Function: Stem cells can regenerate insulin-producing beta cells, potentially restoring normal insulin secretion.
-
Reduced Insulin Dependency: Patients may experience a decrease in the need for exogenous insulin administration.
-
Improved Glycemic Control: Enhanced insulin sensitivity leads to better blood glucose regulation.
-
Potential Reversal of Complications: Stem cell therapy may alleviate or reverse complications associated with diabetes.
-
Minimal Side Effects: When using autologous stem cells, the risk of immune rejection is significantly reduced.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, stem cell therapy for Type 2 diabetes faces several challenges:
-
Standardization of Protocols: There is a lack of universally accepted protocols for stem cell therapy, leading to variability in treatment outcomes.
-
Long-Term Efficacy: The long-term effectiveness and safety of stem cell therapy require further investigation through extensive clinical trials.
-
Cost and Accessibility: The high cost of stem cell treatments may limit accessibility for many patients, though India offers more affordable options compared to Western countries.
-
Regulatory Oversight: Ensuring that stem cell therapies are conducted in compliance with medical regulations is crucial to patient safety.
The Future of Stem Cell Therapy in Diabetes Management
The future of stem cell therapy in Type 2 diabetes management looks promising. Ongoing research aims to refine techniques, improve cell delivery methods, and enhance the scalability of treatments. Advancements in gene editing and tissue engineering may further augment the efficacy of stem cell therapies.
In India, the integration of stem cell therapy into mainstream diabetes care could revolutionize treatment paradigms, offering patients a potential pathway to remission and improved quality of life.
Conclusion
Type 2 Diabetes Stem Cell Therapy in India represents a significant advancement in the treatment of this prevalent chronic condition. By harnessing the regenerative capabilities of stem cells, Indian medical centers are at the forefront of offering innovative therapies that address the root causes of diabetes. While challenges remain, the progress made thus far provides hope for patients seeking more effective and sustainable treatment options.
As research continues and treatment protocols are standardized, stem cell therapy may become an integral component of comprehensive diabetes care, not only in India but globally.